ARC Data Delivery Service Technical Description
This page describes how to set up DTR over multiple hosts.
Introduction
In DTR the transfers can be split over multiple hosts to scale up the data transfer throughput. Remote hosts only perform simple point-to-point transfers between physical endpoints and all the logic is kept in the main A-REX host. This has many advantages:
Keeping all the high-level logic in one place allows intelligent load balancing.
The remote hosts do not do submission to the batch system and so all LRMS configuration only needs to be done in one place.
A problem with a remote host does not mean a lost job - the transfer can simply be retried on another host.
The setup and configuration of a remote host is very simple.
The datadelivery service has been developed within HED and can be deployed on one or many remote hosts. Once a DTR has passed all the pre-processing steps and is ready for transfer, the Scheduler can send it to a remote datadelivery service to execute the transfer. The Scheduler will then poll the request until it has completed. The Scheduler spreads randomly the total number of transfers (up to the configured limit and depending on the configured access rights of each service) between all the staging hosts.
The architecture is shown in the figure below. The datadelivery service on the remote host acts as a very simple Scheduler which sends all transfer requests it receives straight to Delivery.
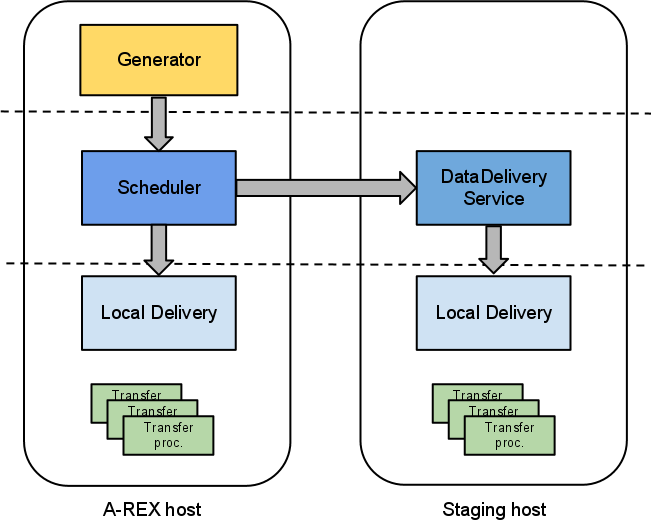
Fig. 18 Multi-host datastaging
Installation
No extra components are necessary on the A-REX host.
For the remote staging hosts, the package nordugrid-arc-datadelivery-service can be found in the usual EPEL or NorduGrid repositories, or is built automatically when building the source tree. This package should be installed on each remote host. It depends on some core ARC packages and the usual external packages that an ARC installation requires. Note that it is not necessary to install A-REX on the staging hosts.
IMPORTANT If support for transfer protocols that are not included in the nordugrid-arc-plugins-base package (e.g. GridFTP or Xrootd) is required then the corresponding plugins packages must also be installed.
CA certificates are required on each remote host to authenticate connections with storage services. Depending on the local set up, each host may also require a host certificate (more info below).
To start|stop the service (as superuser):
systemctl start|stop arc-datadelivery-service
The log file for the service can be found at /var/log/arc/datadelivery-service.log (configurable - see below). If logrotate is running, this log will be rotated every day.
Configuration
Remote Hosts
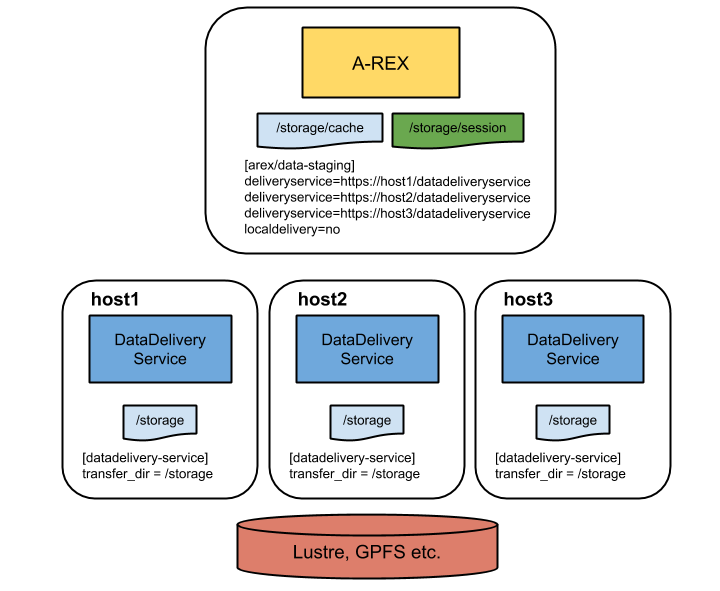
The datadelivery service uses the [datadelivery-service] section of the arc.conf configuration file.
By default the datadelivery service runs with TLS enabled and a host certificate is required for each host. The path to the host credentials may be specified by the usual x509 options. Host certificates are not a strict requirement and it is possible to run without TLS using the secure=no option. This means that A-REX can no longer verify the authenticity of the remote hosts and so the decision to run with or without host certificates should be based on local site policy.
The following configuration options are supported:
Parameter |
Explanation |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|
x509_host_key |
Path to host key |
/etc/grid-security/hostkey.pem |
x509_host_cert |
Path to host cert |
/etc/grid-security/hostcert.pem |
x509_cert_dir |
Path to CA certificates |
/etc/grid-security/certificates |
hostname |
Hostname of service host |
localhost |
port |
Port on which service runs |
443 |
pidfile |
pid file |
/var/run/arched-datadelivery-service.pid |
logfile |
Log file |
/var/log/arc/datadelivery-service.log |
loglevel |
Logging level (0 (FATAL) to 5 (DEBUG)) |
2 (WARNING) |
user |
User under which service runs (should only be changed in special cases) |
root |
secure |
Set to “no” if the service should run without a host certificate |
yes |
allowed_ip |
IP address authorized to access service (can be specified multiple times) |
No default, must be specified |
allowed_dn |
DN authorized to access service (can be specified multiple times) |
No default |
transfer_dir |
Path the service is allowed to read/write to (can be specified multiple times) |
No default, must be specified must be specified |
At least one allowed_ip and at least one transfer_dir are the only mandatory parameters, but it can be useful to change interface, port and loglevel from the default.
Since the service can copy files to and from the service host, it is dangerous to allow open access to any clients. Usually allowed_ip is set to the IP address of the A-REX host since this is the only host which should have access to the service. The service can be further locked down by specifying authorized DNs so that only certain users are allowed to have their jobs’ files staged by the service. Note that DN filtering is not possible if secure=no is specified.
It is also dangerous to allow requests which can copy to or from anywhere on the host filesystem, so filesystem access is restricted through the transfer_dir parameter, which specifies the path(s) that requests are allowed to use. The service is able to read and write to any path matching transfer_dir. transfer_dir(s) should be specified which match every cache and session dir. In some situations it may be desirable to set for example one cache per remote host where the cache is local to the host. A-REX checks on start-up which dirs are accessible by which remote hosts and uses that info to direct the DTRs to the right hosts.
Configuration example:
[datadelivery-service]
loglevel = 3
hostname = delivery.host.1
port = 60002
allowed_ip = 1.2.3.4
transfer_dir = /var/arc/session
transfer_dir = /var/arc/cache
If the site has multiple caches like /var/arc/cache-01, /var/arc/cache-02 etc, then this configuration will allow the delivery service to write to all of them.
It is vital that the cache and session file systems are mounted on the same path on the A-REX and each remote host, as the system assumes that a transfer to the cache or session directory can be done using the same path on all hosts. It is also vital that user accounts are in sync across all hosts, so that a user represented by a uid on the A-REX host maps to the same account on all the remote hosts. No mapping of DN to local user is done on the remote hosts, and so no mapping infrastructure like gridmap files is required. The local user id of the user owning the transfer is passed in the request to the service and the transfer process is executed under that uid (except when writing to cache, when the root account is used).
The service is started and stopped by the arc-datadelivery-service systemd unit:
systemctl start arc-datadelivery-service
A-REX Host
The configuration for setting up A-REX to use remote datadelivery services uses options in the [arex/data-staging] section of the regular arc.conf.
Parameter |
Explanation |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|
deliveryservice |
URL of remote host which can perform data delivery. Hostname and port must match those specified in the datadelivery service configuration. |
None |
localdelivery |
Whether local delivery should also be done |
no |
remotesizelimit |
File size limit (in bytes) below which local transfer is always used |
0 |
usehostcert |
Whether the host certificate should be used in communication with remote datadelivery services instead of the user’s proxy |
no |
Example:
[arex/data-staging]
deliveryservice = https://delivery.host.1:60002/datadeliveryservice
deliveryservice = https://delivery.host.2:60002/datadeliveryservice
localdelivery = yes
remotesizelimit = 1000000
Multiple remote datadelivery services can be specified, and the Scheduler will randomly divide DTRs between those services where the transfer is allowed (according to transfer_dir configuration on each service). The presence of a datadeliveryservice option turns off the regular “local” delivery on the A-REX host so only the remote service will be used. If it is desired to also do transfers on the A-REX host, localdelivery = yes must be used. If no remote services are specified then local delivery is always enabled.
If the datadelivery service is running with secure=no then https should be replaced by http in the deliveryservice URLs.
Normally the credentials of the user who submitted the job are used for communication between A-REX and remote datadelivery services, however for extra security it is possible to use the A-REX host certificate for this instead, by specifying usehostcert = yes. In this case the host cert is only used for establishing the secure connection with the remote service, it is still the user’s credentials which are delegated and used for the transfer. The host cert must also be able to be used as a client certificate, in other words must have the X509 extension “X509v3 Extended Key Usage: TLS Web Client Authentication”. This option has no effect if the datadelivery service is running with secure=no.
Communication with remote services involves some degree of overhead such as the SSL handshake, delegating credentials etc, and when transferring small files this overhead can become a significant fraction of the transfer time. Therefore it is possible to specify a file size limit (in bytes) with remotesizelimit. Any files smaller than this limit will use local transfer, even if local transfer is disabled through localdelivery = no.
Deployment Scenarios
Several ways of deploying multi-host data staging are possible, using any number of remote hosts. Two examples are shown here.
Local Caches
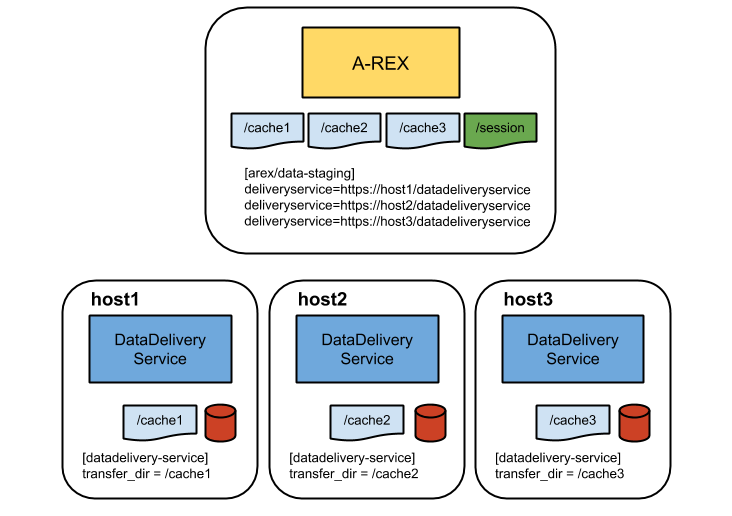
Fig. 20 DDS deployment: local disk for cache on DDS nodes
Each remote host has its own local disk as a cache and these caches are mounted on the A-REX host. DTRs will be sent to the host corresponding to the cache chosen for the DTR so that all cache transfers are to local disks. The session directory is not available on the remote hosts so all uploads and non-cache downloads will run on the A-REX host.
Security
The remote datadelivery service may require a host certificate (see above) and allow incoming connections from the A-REX host, but no other incoming connections are required. It must have outbound connectivity to the world to perform the transfers. As explained above, access is normally restricted to the A-REX host and transfers restricted to the cache and session directories. For each transfer A-REX delegates the credentials of the user who submitted the job to the remote service, which creates a temporary file containing the credentials. This file is deleted when the transfer finishes. Creating a file should become unnecessary if pure in-memory credentials are fully supported by ARC and all transfer protocols.
The transfer process itself is executed under the uid of the session directory owner, unless the transfer is to cache in which case it is executed by root. It is therefore important that user accounts are synchronised across all hosts. The file systems with the cache and session directories must be mounted on the same paths with the same user access rights on all hosts.
Proxies
HED services do not support legacy proxies such as those generated by default by voms-proxy-init. In order to use remote datadelivery services, the jobs must be submitted to A-REX using RFC proxies, which can be generated by arcproxy or giving the option -rfc to voms-proxy-init. If a legacy proxy is used, local transfer will be used even if it is disabled in the configuration.
Monitoring Remote Hosts
When the first DTR is received by the Scheduler, it pings all the configured remote datadelivery services to check that they are running and to get the list of allowed directories from each one. If a service is unreachable it will not be used. If all services are unreachable then local delivery will be used even if it is turned off in the configuration. The allowed directories information is used to direct DTRs to services where the transfer is allowed. This procedure is repeated every 5 minutes (for the first DTR received after the 5 minute limit), and only the successful services are used until the next check (unless none are successful, in which case the check is done for every DTR until one succeeds). This means that configuration changes in the remote hosts will be picked up automatically after some time. However any changes in A-REX’s configuration, such as adding a new remote host, require an A-REX restart to be effective.
If remote datadelivery services are enabled, the number of DTRs assigned to each one can be seen on separate plots in Gangliarc.